Using Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflow on Ubuntu
This post is over a year old, some of this information may be out of date.
In my previous blog post, I explained how you could use the Microsoft’s Dev Proxy in a GitHub Actions workflow on a macOS runner. In this blog post, I will show you how to use the Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflow on an Ubuntu runner.
Most of the steps are the same, except how you trust the root certificate.
Installing and running the Dev Proxy
Like the macOS runner, you can install the bash script provided in the Dev Proxy documentation on the Ubuntu runner. To include this into your GitHub Actions workflow, you can use the following step:
- name: Install Dev Proxy run: bash -c "$(curl -sL https://aka.ms/devproxy/setup.sh)"
- name: Run Dev Proxy run: ./devproxy/devproxy &Once the Dev Proxy is installed, you can run it, but you cannot yet intercept HTTPS traffic. That is where the next step comes in. You need to trust the root certificate.
Trust the root certificate
Similar to the macOS configuration, we must trust the self-signed certificate the Dev Proxy created. Here are the steps to achieve the certificate trust on an Ubuntu runner:
- name: Install the Dev Proxy's certificate timeout-minutes: 1 run: | echo "Export the Dev Proxy's Root Certificate" openssl pkcs12 -in ~/.config/dev-proxy/rootCert.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out dev-proxy-ca.crt -passin pass:""
echo "Installing the Dev Proxy's Root Certificate" sudo cp dev-proxy-ca.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
echo "Updating the CA certificates" sudo update-ca-certificates echo "Certificate trusted."
# Set the system proxy settings (optional) echo "http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:8000" >> $GITHUB_ENV echo "https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:8000" >> $GITHUB_ENVAfter running this step, you can start intercepting HTTPS traffic with the Dev Proxy.
The complete GitHub Actions workflow
Below, you can find the complete GitHub Actions workflow file, which includes the installation of the Dev Proxy and the trust of the root certificate.
name: Ubuntu Dev Proxy
on: push: branches: - main - dev workflow_dispatch:
jobs: test: timeout-minutes: 60 runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
- name: Install Dev Proxy run: bash -c "$(curl -sL https://aka.ms/devproxy/setup.sh)"
- name: Run Dev Proxy run: ./devproxy/devproxy &
- name: Install the Dev Proxy's certificate timeout-minutes: 1 run: | echo "Export the Dev Proxy's Root Certificate" openssl pkcs12 -in ~/.config/dev-proxy/rootCert.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out dev-proxy-ca.crt -passin pass:""
echo "Installing the Dev Proxy's Root Certificate" sudo cp dev-proxy-ca.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
echo "Updating the CA certificates" sudo update-ca-certificates echo "Certificate trusted."
# Set the system proxy settings (optional) echo "http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:8000" >> $GITHUB_ENV echo "https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:8000" >> $GITHUB_ENV
# Include the additional steps you want to run after the Dev Proxy started - name: Test the Dev Proxy run: | curl -ix http://127.0.0.1:8000 https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts # When you used the system proxy settings, you don't need to specify the proxy in the curl command curl -i https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts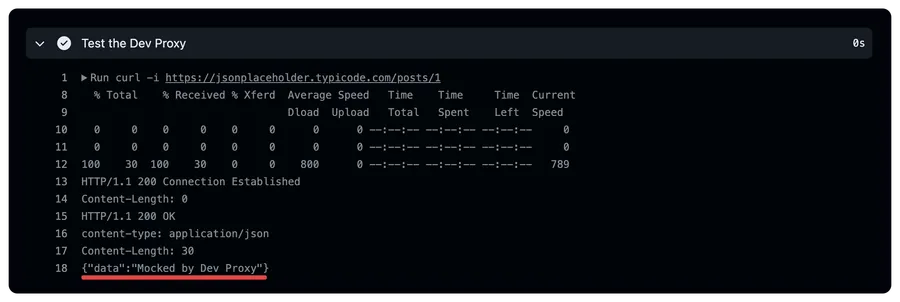
With this setup, you can use the Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflow on a Ubuntu runner.
Related articles
Using Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflow on macOS
Learn how to use Dev Proxy in a GitHub Actions workflow on macOS hosted VM for intercepting and inspecting your API calls
Caching Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflows
Learn how to cache the Dev Proxy in your GitHub Actions workflows. This allows you to reuse the Dev Proxy installation and speed up your workflow.
Use Playwright with Microsoft Dev Proxy on GitHub Actions
Learn how to use Playwright with Microsoft Dev Proxy on GitHub Actions to easily test your solutions with the same mocked API responses as during development.
Report issues or make changes on GitHub
Found a typo or issue in this article? Visit the GitHub repository to make changes or submit a bug report.
Comments
Let's build together
Manage content in VS Code
Present from VS Code
Engage with your audience throughout the event lifecycle
